EPILEPSY

Diagnosing your condition
EEG brain activity

CT scan
Pinpointing seizure location
To diagnose epilepsy, your healthcare professional reviews your symptoms and medical history. You may have several tests to diagnose epilepsy and to detect the cause of seizures. They may include:
A neurological exam. This exam tests your behavior, movements, mental function and other areas. The exam helps diagnose epilepsy and determine the type of epilepsy you may have.
Blood tests. A blood sample can detect signs of infections, genetic conditions or other conditions that may be associated with seizures.
Genetic testing. In some people with epilepsy, genetic testing may give more information about the condition and how to treat it. Genetic testing is most often performed in children but also may be helpful in some adults with epilepsy.
You also may have brain imaging tests and scans that detect brain changes:
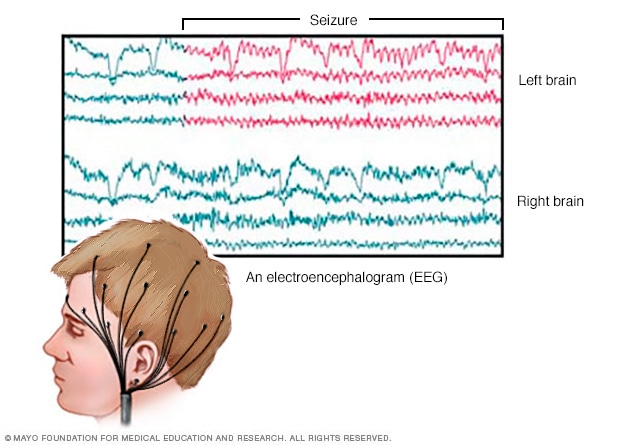
Electroencephalogram (EEG). This is the most common test used to diagnose epilepsy. In this test, small metal discs called electrodes are attached to your scalp with an adhesive or cap. The electrodes record the electrical activity of your brain.If you have epilepsy, it's common to have changes in the pattern of brain waves. These changes occur even when you're not having a seizure. Your healthcare professional may monitor you on video during an EEG to detect and record any seizures. This may be done while you're awake or asleep. Recording the seizures may help determine what kind of seizures you're having or rule out other conditions.The test may be done in a healthcare professional's office or the hospital. Or you may have an ambulatory EEG. The EEG records seizure activity over the course of a few days at home.You may get instructions to do something that can cause seizures, such as getting little sleep prior to the test.
High-density EEG. In a variation of an EEG test, you may have a high-density EEG. For this test, electrodes are placed closer together compared with a conventional EEG. High-density EEG may help more precisely determine which areas of your brain are affected by seizures.
Computerized tomography (CT) scan. A CT scan uses X-rays to obtain cross-sectional images of your brain. CT scans can detect tumors, bleeding or cysts in the brain that might be causing epilepsy.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create a detailed view of the brain. Like a CT scan, an MRI looks at the structure of the brain to detect what may be causing seizures. But an MRI provides a more detailed look at the brain than a CT scan.
Functional MRI (fMRI). A functional MRI measures the changes in blood flow that occur when specific parts of the brain are working. This test may be used before surgery to identify the exact locations of critical functions, such as speech and movement. This allows surgeons to avoid those areas while operating.
Positron emission tomography (PET). PET scans use a small amount of low-dose radioactive material. The material is injected into a vein to help visualize metabolic activity of the brain and detect changes. Areas of the brain with low metabolism may indicate places where seizures occur.
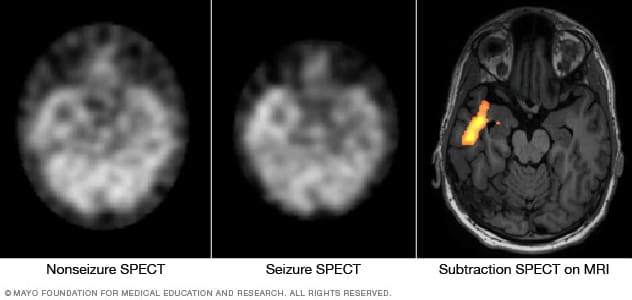
Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT). This type of test is used if MRI and EEG didn't pinpoint the location in the brain where the seizures start.A SPECT test uses a small amount of low-dose radioactive material. The material is injected into a vein to create a detailed, 3D map of blood flow during seizures. Areas of higher than typical blood flow may indicate areas where seizures occur.Another type of SPECT test called subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered to MRI (SISCOM) may provide even more-detailed results. The test overlaps the SPECT results with brain MRI results.
Neuropsychological tests. These tests assess thinking, memory and speech skills. The test results help determine which areas of the brain are affected by seizures.
Along with your test results, a combination of other techniques may be used to help pinpoint where in the brain seizures start:
Statistical parametric mapping (SPM). SPM looks at the areas of the brain with increased blood flow during seizures. It's compared to the same areas of the brains of people who don't have seizures. This provides information about where seizures begin.
Electrical source imaging (ESI). ESI is a technique that takes EEG data and projects it onto an MRI of the brain. This is done to show areas where seizures are occurring. This technique provides more-precise detail than does EEG alone.
Magnetoencephalography (MEG). MEG measures the magnetic fields produced by brain activity. This helps find the potential areas where seizures start. MEG can be more accurate than EEG because the skull and tissue surrounding the brain interfere less with magnetic fields. MEG and MRI together provide images that show areas of the brain both affected by seizures and not affected by seizures.
Diagnosis of your seizure type and where seizures begin gives you the best chance for finding an effective treatment.
Treatment
Treatment can help people diagnosed with epilepsy have fewer seizures or even completely stop having seizures. Possible treatments include:
Medicines.
Surgery.
Therapies that stimulate the brain using a device.
A ketogenic diet.
Medication
Most people with epilepsy can become seizure-free by taking one anti-seizure medicine, which is also called an anti-epileptic medicine. Others may be able to decrease the number and intensity of their seizures by taking more than one medicine.
Many children with epilepsy who aren't having epilepsy symptoms can eventually stop taking medicines and live a seizure-free life. Many adults can stop taking medicines after two or more years without seizures. Your healthcare team can advise you about the appropriate time to stop taking medicines.
Finding the right medicine and dosage can be complex. Your provider may consider your condition, how often you have seizures, your age and other factors when choosing which medicine to prescribe. Your provider also may review any other medicines you may be taking to ensure the anti-seizure medicines won't interact with them.
You may first take a single medicine at a low dose. Then your healthcare professional may increase the dosage gradually until your seizures are well controlled.
There are more than 20 different types of anti-seizure medicines available. The medicines that you take depend on the type of seizures you have, your age and other health conditions.
Anti-seizure medicines may have some side effects. Mild side effects include:
Fatigue.
Dizziness.
Weight gain.
Loss of bone density.
Skin rashes.
Loss of coordination.
Speech problems.
Memory and thinking problems.
More-serious but rare side effects include:
Depression.
Suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Severe rash.
Inflammation of certain organs, such as the liver.
For the best seizure control possible with medicine, follow these steps:
Take medicines exactly as prescribed.
Always call your healthcare professional before switching to a generic version of your medicine or taking other medicines. This includes medicines you get with or without a prescription and herbal remedies.
Never stop taking your medicine without talking to your healthcare professional.
Tell your healthcare professional immediately if you notice new or increased feelings of depression or suicidal thoughts. Also contact your healthcare professional right away if you have changes in your mood or behaviors.
Tell your healthcare professional if you have migraines. You may need an anti-seizure medicine that can prevent your migraines and treat epilepsy.
At least half the people newly diagnosed with epilepsy become seizure-free with their first medicine. If anti-seizure medicines don't provide good results, you may be able to have surgery or other therapies. You'll likely have regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional to check on your condition and medicines.
Surgery
 Epilepsy surgery
Epilepsy surgery
When medicines do not provide enough control of seizures, epilepsy surgery may be an option. With epilepsy surgery, a surgeon removes the area of your brain that's causing seizures.
Surgery usually is done when tests show that:
Your seizures start in a small, well-defined area of your brain.
The surgery wouldn't affect vital functions such as speech, language, movement, vision or hearing.
For some types of epilepsy, minimally invasive approaches such as MRI-guided stereotactic laser ablation may help symptoms. These treatments may be used when open surgery is too risky. This procedure involves using a thermal laser probe directed at the area in the brain causing seizures. It destroys tissue in an effort to better control the seizures.
You may continue to take medicine to help prevent seizures after successful surgery. However, you may be able to take fewer medicines and reduce your doses.
In a small number of people, surgery for epilepsy can cause complications. Complications may include a permanent change in thinking abilities. Talk to your surgical team members about their experience, success rates and complication rates with the procedure you're considering.
Therapies
Vagus nerve stimulation
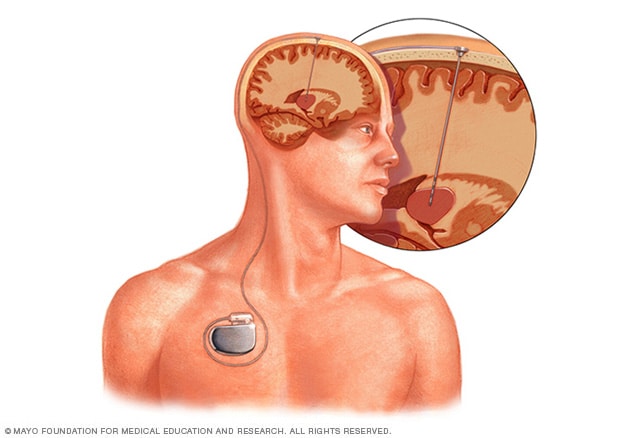
Deep brain stimulation
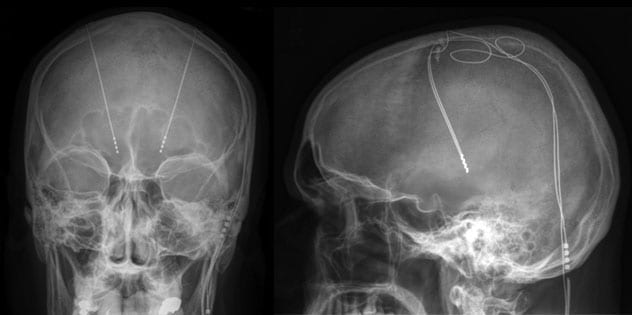
MRI of deep brain stimulation
Apart from medicines and surgery, these potential therapies offer an alternative for treating epilepsy:
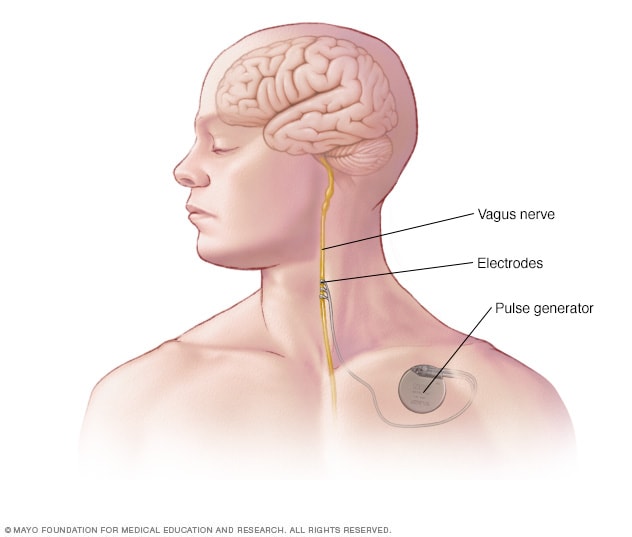
Vagus nerve stimulation. Vagus nerve stimulation may be an option when medicines haven't worked well enough to control seizures and surgery isn't possible. A device called a vagus nerve stimulator is implanted underneath the skin of the chest, similar to a heart pacemaker. Wires from the stimulator are connected to the vagus nerve in the neck.The battery-powered device sends bursts of electrical energy through the vagus nerve and to the brain. It's not clear how this inhibits seizures, but the device can usually reduce seizures by 20% to 40%.Most people still need to take anti-seizure medicine. But some people may be able to lower their medicine dose. Vagus nerve stimulation side effects may include throat pain, hoarse voice, shortness of breath or coughing.
Deep brain stimulation. In deep brain stimulation, surgeons implant electrodes into a specific part of the brain, typically the thalamus. The electrodes are connected to a generator implanted in the chest. The generator regularly sends electrical pulses to the brain at timed intervals and may reduce seizures. Deep brain stimulation is often used for people whose seizures don't get better with medicine.
Responsive neurostimulation. These implantable, pacemaker-like devices can help reduce how often seizures occur. The devices analyze brain activity patterns to detect seizures as they start. They deliver electrical stimulation to stop the seizure. Research shows that this therapy has few side effects and can provide long-term seizure relief.
Ketogenic diet
Some children and adults with epilepsy reduce their seizures by following a diet high in fats and low in carbohydrates. This may be an option when medicines aren't helping to control epilepsy.
In this diet, called a ketogenic diet, the body breaks down fats instead of carbohydrates for energy. After a few years, some children may be able to stop the ketogenic diet and remain seizure-free. It's important for this to be done under close supervision of healthcare professionals.
Experts don't fully know how a ketogenic diet works to reduce seizures. But researchers think that the diet creates chemical changes that suppress seizures. The diet also alters the actions of brain cells to reduce seizures.
Get medical advice if you or your child is considering a ketogenic diet. It's important to make sure that your child gets enough nutrients when following the diet.
Side effects of a ketogenic diet may include dehydration, constipation and slowed growth from not getting enough nutrition. Side effects also may include a buildup of uric acid in the blood, which can cause kidney stones. These side effects are not common if the diet is properly and medically supervised.
Following a ketogenic diet can be hard. Low-glycemic index and modified Atkins diets offer less restrictive alternatives that may still provide some help for seizure control.
Potential future treatments
Researchers are studying many potential new treatments for epilepsy, including:
Continuous stimulation of the seizure onset zone, known as subthreshold stimulation. Subthreshold stimulation is continuous stimulation to an area of the brain below a level that's physically noticeable. This type of therapy appears to improve seizure outcomes and quality of life for some people with seizures. Subthreshold stimulation helps stop a seizure before it happens.This treatment may work in people who have seizures that start in an area of the brain called the eloquent area. This area can't be removed because it would affect speech and movements. Or it might help people with seizure types that may not improve with responsive neurostimulation.
Minimally invasive surgery. New minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as MRI-guided focused ultrasound, show promise for treating seizures. These surgeries have fewer risks than traditional open-brain surgery for epilepsy.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). TMS applies focused magnetic fields on areas of the brain where seizures occur to treat seizures without the need for surgery. It may be used for patients whose seizures occur close to the surface of the brain and can't be treated with surgery.
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). This technique provides electrical stimulation through the scalp to the brain to reduce seizures over time. This treatment may be provided at home.
